Heat is a common term we encounter in our daily life. Heat is a type of energy like kinetic energy, potential energy, chemical energy, etc. Heat energy can be easily felt and also can be easily measured by a quantity called temperature.
There is everywhere heat is used like cooking of food on gas- cylinder, in the oven, in the heater, iron for clothes, also in the industry for the reactor, drying, in the concentrator, for various reactions, heat exchangers, furnaces, condenser, refrigeration, sterilizing, for preheating heat is required.
What is Heat Transfer?
Heat transfer is called "Heat transfer". Heat transfer takes place because of the temperature difference between the two systems. Mostly related to thermodynamic concepts of heat generation, the conversation one to another form, and exchange with cold to hot or vice versa.
Types (Modes) of Heat Transfer
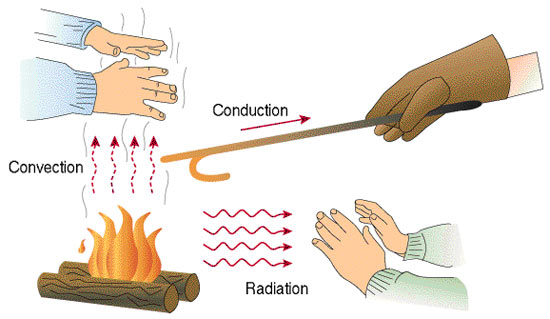
Heat is transferred in three different modes:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
Let's take a look one by one.
(1) Conduction: It is the transfer of energy or heat from high to lower energy systems. Conduction takes place because of molecular collision and can occur in solid, liquid, and gases. In solids, conduction is because of the vibration of molecules and the free energy of electrons. In liquid and gases, conduction takes place in molecular diffusion and collision of molecules during random motion.
The rate of heat conduction is directly proportional to temperature difference, area of conduction, and inversely proportional to the thickness of the conducting layer. This statement is called " Fourier's law of heat conduction".
Q = -K*A ∆T/∆xWhereK= Proportionality constant called thermal conductivity of the material. Which is measured of ability to conduct the heat of materialA= Heat transfer area∆T/∆x = Is called Temperature gradient, Negative sign shows temperature gradient decreases with the thickness of the heat transfer layer.
Examples:
Hot tea makes the cup itself hot.
Ice cubes melt if we put them into our palm where heat transfer takes place from hand to ice.
Heat transfer from burner to the pan.
Ironing clothes.
Indirect heat exchanger where heat transfer takes place between hot and cold fluid without touching each other.
(2) Convection: In this mode heat transfer takes place between the solid surface and moving fluid. If the fluid motion is higher than greater the convection rate.
Convection is further classified into two types based on how fluid motion over a solid surface is given.
Forced convection: In this fluid motion over the solid surface for convection is given by external forces like a fan, pump, blower, etc.
Natural or free convection: In this fluid motion is caused by buoyancy force which is due to density difference because of the variable temperature in fluid. Here no external forces are given that's why it's called natural convection.
"Rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to temperature difference and area of heat transfer" this statement is called Newton's law of cooling.
Q = hA(Ts - To)Where,h = Convection heat transfer coefficient, Proportionality constantA= Heat transfer areaTs = Surface temperature solidTo = surrounding temperature (fluid temperature)
Examples:
- Air conditioning.
- Boiling of water where heat transfer takes place from pan to water.
- Melting of ice in the surrounding.
- From chimney hot air went bottom to top.
- Car radiator using fluid.
- Convection oven.
(3) Radiation: It is the energy emitted by matter in the form of electromagnetic waves. Radiation can occur without a medium, for example, solar energy can come to the earth without a medium. Radiation is generally taken as a surface phenomenon.
Maximum radiation emitted by the surface is given by "Stefan Boltzmann law".Q = σAT⁴Where,σ = Stefan Boltzmann constant
Important terms used in radiation
Blackbody: The idealized surface which emits the maximum rate called "Blackbody".
Emissivity: It's a measure of how close the real surface is to the Blackbody.
Absorptivity: It's a fraction of how much radiation incident and how the surface has absorbed the radiation.
Examples:
- Ultraviolet light from the sun.
- The heat from a lightbulb.
- The heat from a fire.
- X-rays
- Microwave from the microwave oven.
- Electromagnetic radiation from mobile.
- Radio-waves.
Applications of Heat Transfer
- There are various applications of heat transfer :
- In air conditioning systems
- Temperature measurement devices like thermometers
- In power plant for electricity generation
- As refrigeration systems in food industries
- Circuit boards in devices like computers, T.V, VCR, etc.
- Radiator in the vehicle