A chemical reactor is the heart of chemical industries. Designing and performance evaluation of chemical reactors are the main aims for chemical engineers.
Knowledge of chemical reactors makes chemical engineers stand apart from other engineering streams. Knowing about chemical reactors is essential for chemical engineers. So, I decided to write a full post about Chemical Reactors.
In this post, we will learn
What is a chemical reactor?
A chemical reactor is a piece of equipment in which a chemical reaction takes place and converts low-value raw materials to high-value products. Chemical reactors are designed according to the rate of reaction which is being carried out in the reactor.
In sort, chemical reactors are vessels that are used to carry out chemical reactions.
For different types of reactions, the rate of reaction is different. So for different types of reactions, different types of reactors are used. It is the chemical engineer's duty to design the best performing and most economical reactor for particular reaction and process conditions.
Parameters that affect the design and performance of the chemical reactors are
- Rate of reaction
- Volume of reactor
- The concentration of Reactants and Products
- The residence time of the reactor
- Heat of reaction
- Operating conditions such as pressure, temperature, etc.
Types of Chemical Reactors
There are three categories in which reactors are classified
- Batch Reactors
- Semi Batch Reactors
- Continuous Reactors
Batch Reactor
A batch reactor is one of the simplest chemical reactors. A batch reactor is just a vessel with an agitator fitted at the top.
First of all, Raw materials are charged in a batch reactor. After charging complete raw material, all inlet valves are closed. a chemical reaction takes place inside the reactor. All molecules spend the same amount of time inside the reactor. The agitator continuously rotates inside the reactor and mixes the mixture. Mixing increases the contact of molecules which increases reaction. After sufficient time is provided for reaction, outlet valves are opened to take out products from the reactor. Sometimes cooling or heating jacket is provided for exothermic or endothermic reactions.
Batch reactors are expensive to operate and also expensive. Also, product quality is variable due to its unsteady behavior.
A batch reactor is also called an unsteady state reactor because the concentration of mixture changes continuously with time in the reactor.
Applications of Batch Reactor
Batch reactors are often used in small-scale processing such as in laboratories to carry out some chemical and biochemical reactions. Also, Batch reactors are widely used in pharmaceutical industries and wastewater treatment plants.
Semi Batch Reactor
Semi batch reactors are a special type of batch reactor in which one reactor is charged at the beginning of the reactor. Then other reactant flows continuously to the reactor. Semi batch reactor is in between batch and continuous reactor, It consists of combined characteristics of both reactor types.
Continuous Reactors
Continuous reactors are vessels or tubes in which reactants flows continuously, spend some time in the reactor, required conversion takes place in the reactor. All molecules may or may not be spent the same amount of time in the reactor.
According to the flow pattern of reactants in chemical reactors, Reactors are classified as
- Plug flow reactor (PFR)
- Mixed flow reactor (MFR)
- Recycle reactor
- Packed bed reactor
- Fluidized bed reactor
- Trickle bed reactor
Plug Flow Reactor (Tubular Reactor)
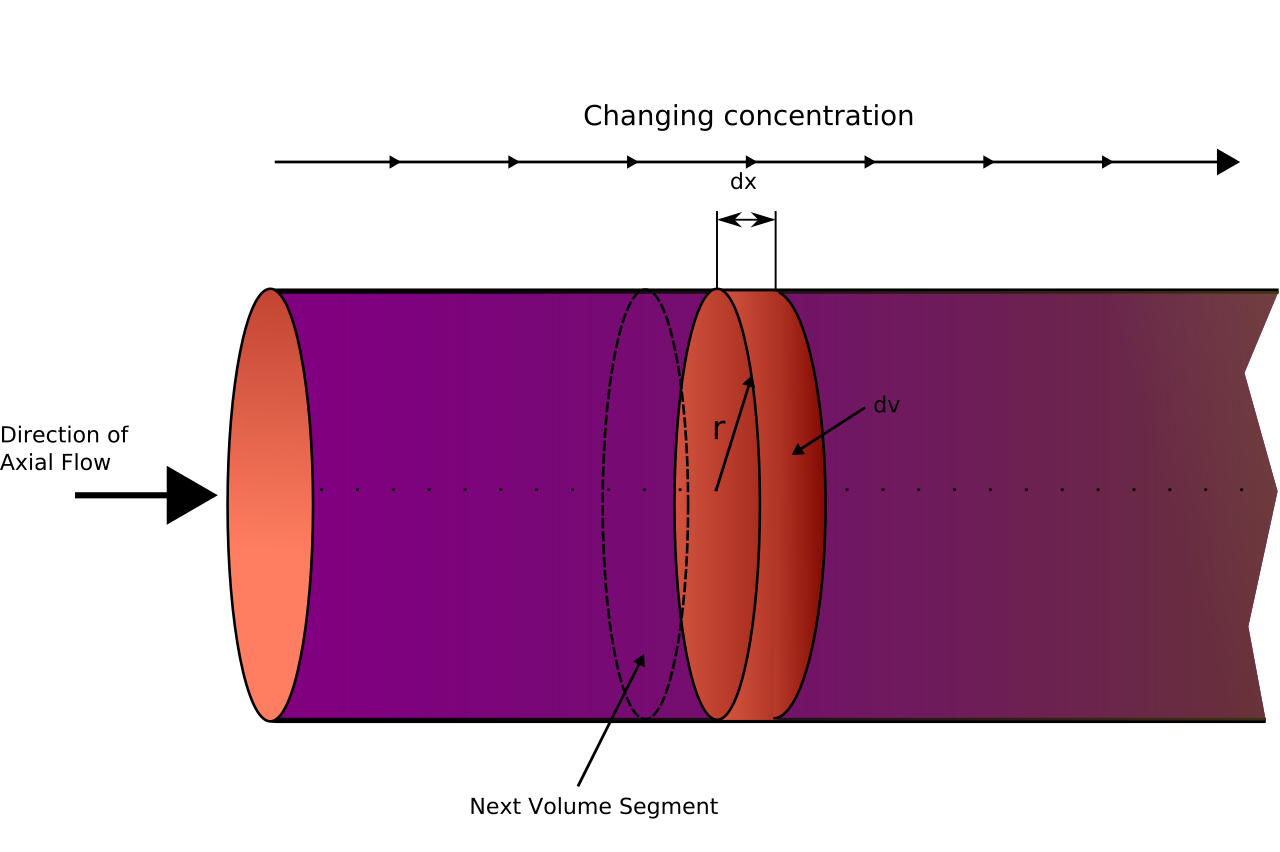
Plug flow reactor consists of tubes in which reactants flow. At one end of the tube, reactants enter. Flows through tubes and spends some time and reaction takes place.
In an ideal plug flow reactor, No axial mixing takes place. Reactants pass as disks passing through the reactor. Reactants react with molecules with the same disk. Reactant's' concentration changes with the length of the plug flow reactor.
The plug flow reactor is the most efficient reactor for reactions with positive order. Because Concentration drops gradually throughout the reactor.
Mixed Flow Reactor (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor)
A mixed flow reactor (MFR) is also called a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR). A continuous stirred tank reactor has the same construction as a batch reactor. It consists of a tank with an agitator.
In MFR (CSTR), the Reactant enters the reactor continuously. Reactant falls on a pool of reaction mixture and continuously product stream comes out.
The ideal mixed flow reactor works as a steady-state reactor. For higher reaction completion, CSTRs are used in series. Different molecules spent different times in the reactor. So some molecules may leave the reactor as comes in and some molecules kept inside reaction mixtures.
Recycle Reactor
Recycle reactor is a special type of plug flow reactor with recycle stream added at the outlet. In recycle reactor, reactants enter and get mixed with recycle stream coming in. This mixed stream enters the plug flow reactor. As reaction mixture comes out from the outlet of plug flow reactor. From the outlet of the reactor, the stream is taken out and sent back to the inlet as a reactant.
Recycling the reactor helps in converting more molecules but also reduces the rate of reaction because reactants get diluted as outlet stream add-in. Especially for autocatalytic reactions, Recycle reactor is the best because in the autocatalytic reaction product of the reaction act as an autocatalytic reaction.
Packed Bed Reactor
A packed bed reactor is a tubular reactor that contains catalyst particles on which both gas and liquid reactants come into contact and a reaction takes place. The packed bed is consists of a bed of catalysts that provide a contact area for liquid and gas reactants and also increase the rate of reaction.
Packed bed reactors are commonly used for the catalytic gas-liquid reaction. Different types of packings are used based on cost and efficiency.
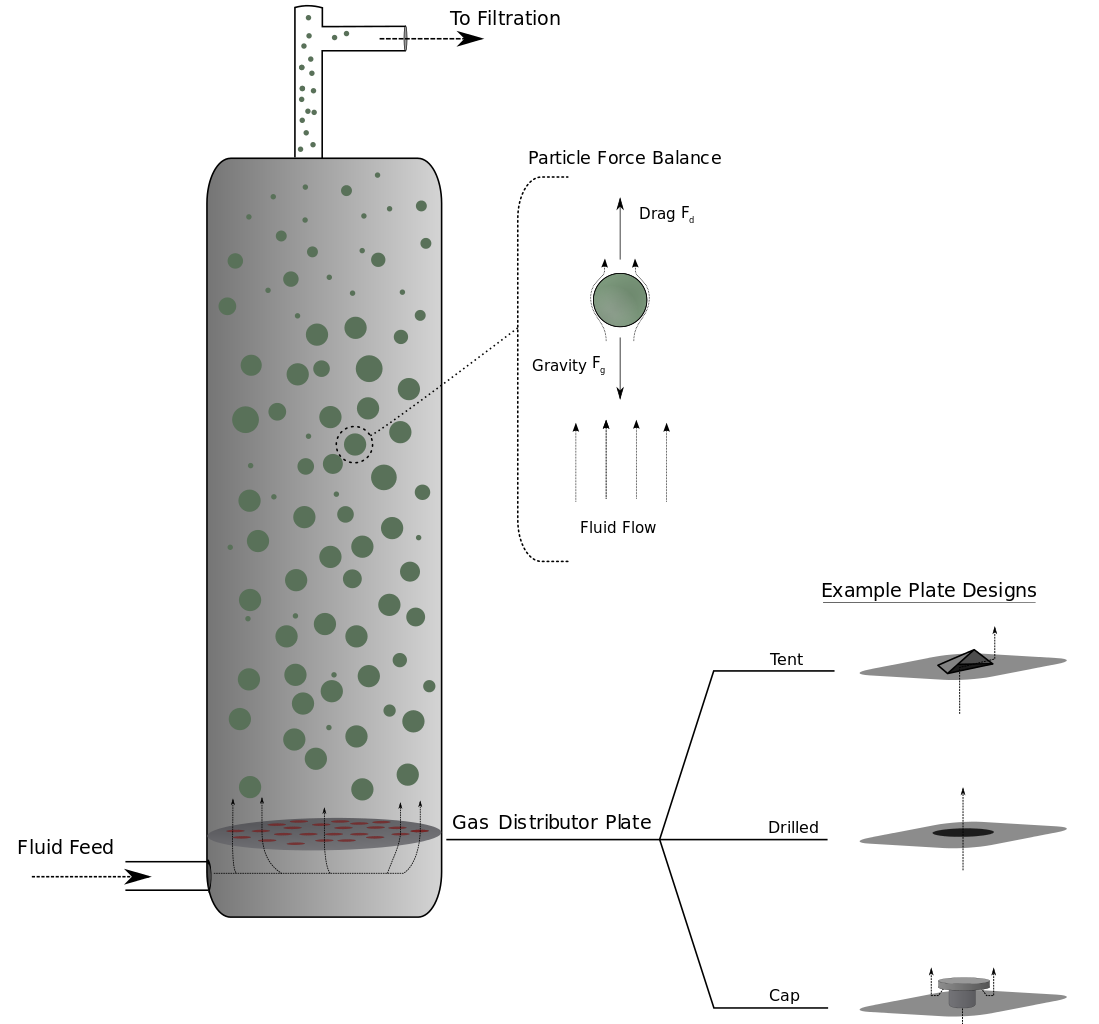
Fluidized Bed Reactor
A fluidized bed reactor is consists of a bed of powder of moderately light particles. These particles are catalysts. In a fluidized bed, gas velocities are so high so that the bed of powder can be lifted. A lifted bed provides a higher surface area for reaction. Generally, a Fluidised bed reactor is used only for gas-phase reactants. Gas reactants come into contact with each other and catalyst in the reactor.
A fluidized bed reactor is best for gas-gas contact catalytic reactions. For example, Catalytic cracking is carried out in petroleum refining in a fluid catalytic cracker which is the fluidized reactor.
Trickle Bed reactor
A trickle bed reactor is a special type of packed bed reactor. A trickle bed reactor is different from a packed bed reactor because the flow of liquid is not continuous but trickling.
Trickle bed reactor consists of beds of catalysts from where gas and liquid come into contact. The reaction takes place on the surface of the catalysts and leaves the bed.




Thanks for sharing great knowledge with us through this blog. Contact Plunes Healthcare, if you are looking for cancer treatment chemotherapy at a discount of upto 50%. Book your free consultation today with the best doctors near you through Plunes Healthcare App.
ReplyDelete