In the atmospheric distillation unit, the Separation of the heavier fraction is not very efficient and economical. To separate heavier fraction into a different fraction we require more energy input.
Two major solutions can be used to separate heavier fractions:
- Increasing temperature: Heavier fraction can be separated by providing extra heat in the furnace which increases the temperature of crude oil and separates heavier fractions. There is one major drawback of this method, By increasing the temperature of crude oil, there are chances of cracking of different fractions.
- Decreasing pressure: By reducing the pressure, We can decrease the boiling point of the components. So by reducing the pressure of the system we can separate heavier components into fractions by application of heat without cracking of components.
Suggested Read: A Beginner's Guide of Distillation
What is Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum distillation is a distillation operation carried out in a vacuum (pressure less than atmospheric pressure) for materials that have a high boiling point (very low vapour pressures) or materials that may degrade near to their boiling point.
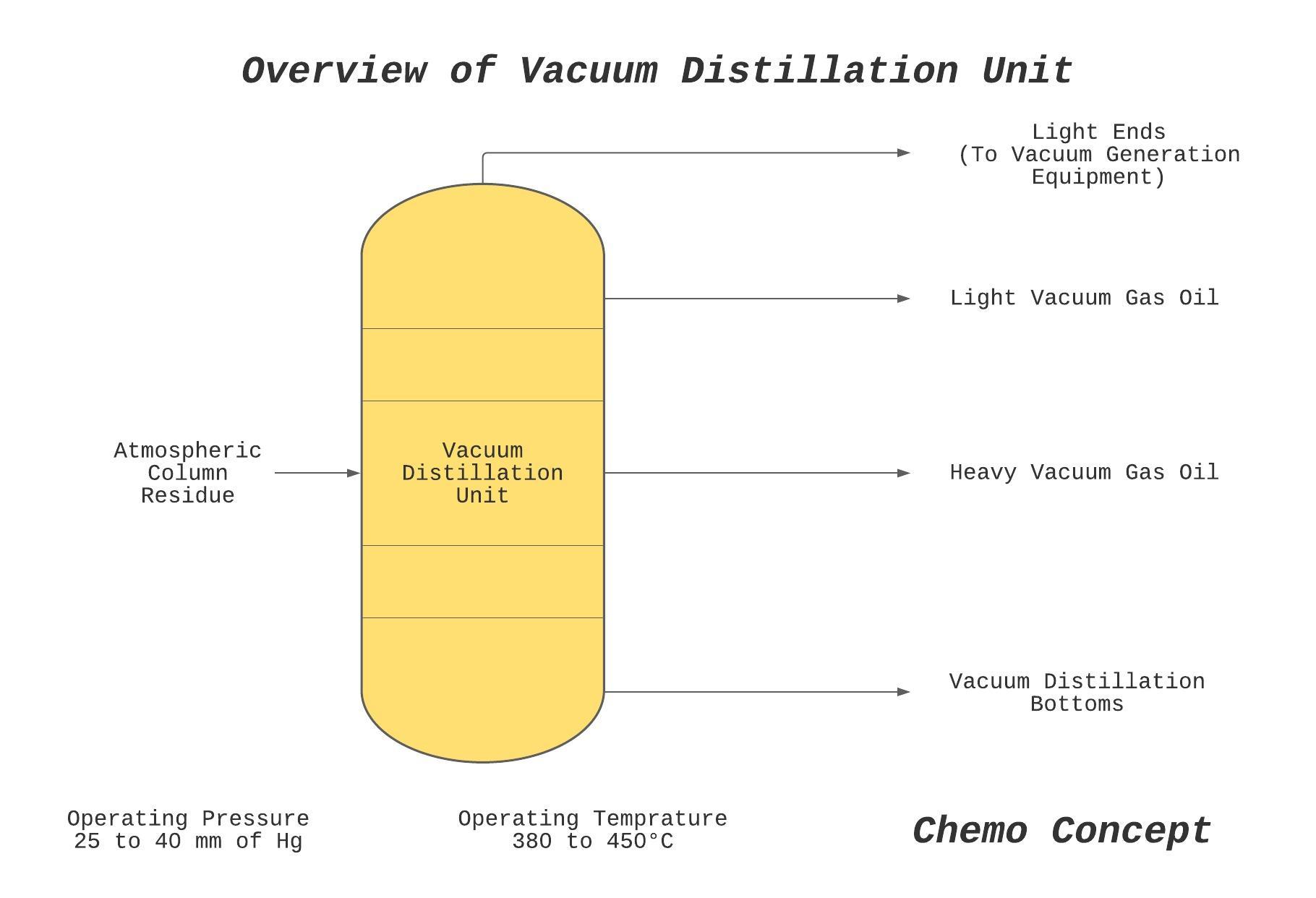
Vacuum Distillation Operation
Distillation is carried out at lower pressures (about 25 to 40 mm of Hg abs). If required pressure can be further decreased by the addition of steam at the furnace inlet and bottom of the distillation unit.
The addition of steam is very beneficial because it not only increases the velocity of petroleum fraction in the furnace tube and also minimizes coke formation in the furnace. Also, steam decreases the partial pressure of petroleum fraction which makes the separation more efficient.
Factors affect Vacuum Distillation Unit Design and Operation
Three major parameters affect distillation operation
- Boiling range of the feed
- Pressure inside column
- Furnace outlet temperature
Vacuum distillation is generally carried out for atmospheric column bottoms and separated into light gas oil and heavy gas oil. Also, light ends and heavy bottoms are produced in the vacuum distillation unit.
The furnace outlet temperature would be 380 to 450°C. Depending on the requirement different outlet temperature can be achieved by changing the steam flow rate in the column or furnace. There are three configurations:
- Dry Operation: In this operation, No steam is added in the inlet of the furnace and at the bottom of the column to get the maximum outlet temperature of petroleum fractions.
- Wet operation: In this operation, Steam is added at the inlet of the furnace and at the bottom of the column to get the minimum outlet temperature of petroleum fractions.
- Damp Operation: In this operation, Steam is only added to the furnace inlet to get the temperature in between temperature achieved by dry operation and wet operation.
By lowering the pressure inside a column, Separation can be improved. To lower the pressure inside column equipment such as steam ejector and barometric condenser or vacuum pump and surface condenser is used.
Conclusion
Further Also Check Out: (Previous Article on This Series)